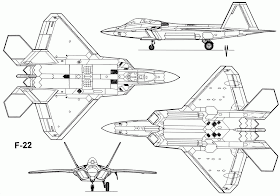
Army and Weapons | F-22 Raptor | F-22 Raptor, The Lockheed Martin/Boeing F-22 Raptor is a single-seat, twin-engine fifth-generation supermaneuverable fighter aircraft that uses stealth technology. . Program partner Boeing Defense, Space & Security provides the wings, aft fuselage, avionics integration, and training systems.Despite a protracted and costly development period, the United States Air Force considers the F-22 a critical component of U.S. tactical air power, and claims that the aircraft is unmatched by any known or projected fighter, while Lockheed Martin claims that the Raptor's combination of stealth, speed, agility, precision and situational awareness, combined with air-to-air and air-to-ground combat capabilities, makes it the best overall fighter in the world today.
The high cost of the aircraft, a lack of clear air-to-air combat missions because of delays in the Russian and Chinese fifth-generation fighter programs, a U.S. ban on Raptor exports, and the ongoing development of the planned cheaper and more versatile F-35 resulted in calls to end F-22 production. The Raptor fleet has resumed flight operations, but problems with the oxygen systems have continued to be reported.
Production termination
Production termination
In December 2007, the USAF requested continued production beyond the planned 183 F-22s.
On 24 September 2008, Congress passed a defense spending bill funding continued production of the F-22. On 5 January 2001, Raptor 4005 flew with the Block 3.0 software, which was the first combat-capable avionics version.[100] In June 2009, Increment 3.1 was tested at Edwards Air Force Base. This provided a basic ground-attack capability through Synthetic Aperture Radar mapping,
Electronic attack and the GBU-39 Small Diameter Bomb. The Increment 3.1 Modification Team with the 412th Test Wing received the Chief of Staff Team Excellence Award for upgrading 149 Raptors. The fleet upgrade should start at the end of 2011.[103] An additional $808 million will be spent in 2013 to implement the 3.1 upgrade. The first upgraded aircraft were delivered in early 2012. F-22 Raptor Andrews Air-force Base Upgrading the first 183 aircraft to the 3.2 upgrade is estimated to cost $8 billion.The F-22 Raptor is a fifth generation fighter that is considered a fourth-generation stealth aircraft by the USAF. Its dual afterburning Pratt & Whitney F119-PW-100 turbofans incorporate pitch axis thrust vectoring, with a range of ±20 degrees.
Avionics
The F-22's avionics include BAE Systems E&IS radar warning receiver (RWR) AN/ALR-94,[151] AN/AAR 56 Infra-Red and Ultra-Violet MAWS (Missile Approach Warning System) and the Northrop Grumman AN/APG-77 Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) radar. ." It has a greater range (250+ nmi) than the radar, allowing the F-22 to limit its own radar emissions to maximise stealth. The AN/APG-77 AESA radar The AN/APG-77 radar, designed for air superiority and strike operations, features a low-observable, active-aperture, electronically-scanned array that can track multiple targets in any weather. The AN/APG-77 changes frequencies more than 1,000 times per second to lower interception probability. Additionally, radar emissions can be focused in an electronic-attack capability to overload enemy sensors. The radar's information is processed by two Raytheon Common Integrated Processor (CIP)sThe radar has an estimated range of 125–150 miles, though planned upgrades will allow a range of 250 miles (400 km) or more in narrow beams.
Cockpit
The F-22 uses a glass cockpit with no analog flight instruments. A side-stick controller and two throttles are the main flight controls. The stick is force sensitive and has limited movement. The cockpit interior lighting is fully night-vision goggle compatible. The monochrome head-up display by GEC (which has since become BAE Systems) offers a wide field of view and serves as a primary flight instrument for the pilot; information is also displayed upon six color liquid crystal display (LCD) panels.
The integrated control panel (ICP) is a keypad system for entering communications, navigation, and autopilot data. The ejection seat is a version of the ACES II (Advanced Concept Ejection Seat) commonly used in USAF aircraft, with a center-mounted ejection control. Carrying missiles and bombs internally maintains its stealth capability and maintains lower drag resulting in higher top speeds and longer combat ranges. This reduces the Raptor's chance of detection by enemy radar systems due to launched ordnance and also allows the F-22 to launch long range missiles while maintaining supercruise. The cannon fire is tracked by the aircraft's radar and displayed on the pilot's heads up display
Stealth
The F-22 was designed to disguise its infrared emissions, reducing the threat of infrared homing ("heat seeking") surface-to-air or air-to-air missiles, including its flat thrust vectoring nozzles.. Furthermore, the F-22 has a Signature Assessment System, which presents warning indicators when normal wear-and-tear degrades the aircraft's radar signature to the point of requiring substantial repair work.
Variants
YF-22A – pre-production version used for ATF testing and evaluation. Two were built.
F-22A – single-seat production version. Was designated "F/A-22A" in early 2000s.
F-22B – planned two-seat variant, but was dropped in 1996 to save development costs.